In December 2016 I made a sketch design of an area magic square to illustrate a seasonal greetings card for 2017. Using the traditional order-3 magic square, I attempted to use continuous straight lines for the area cell borders. I quickly realised that such an assembly was impossible to achieve, but that with approximate areas I could nevertheless make a pleasing graphic pattern:
Sending this image with my best wishes to a circle of magic square enthusiasts on the 30th December 2016, I added the following postscript: "The areas are approximate, and I don't know if it is possible to obtain the correct areas with 2 vertically slanted straight lines through the square. Perhaps someone will be able to work this out in 2017?"
Lee Sallows was the first to respond on the 4th and 5th January 2017, proposing an approach based on his previous work on geomagic squares. Developing the ideas that can be found in the figure 4.1 on page 5 of his book
"Geometric Magic Squares: A Challenging New Twist Using Colored Shapes Instead of Numbers," his area square is illustrated below:
 |
| Area square by Lee Sallows |
Lee Sallows points out that, when comparing the initial square of his book with this new puzzle square, "in many (but not all) cases adjacent piece outlines have been made to complement each other. For every gain in area at one position there is an identical loss of area at another. In this way the areas of all 9 pieces remain as they were, so that the square remains a magical dissection." Thank you for your work Lee! I particularly like your puzzle solution.
Meanwhile, I was wondering if a solution could be found for a third-order area magic torus, that is to say, one where the area cell intersections would meet correctly when wrapped. With this purpose in mind I set the following new rules for myself:
1/ Each cell will have an area that corresponds with its number from 1 to 9. The total areas will therefore be 45.
2/ The connections between the cells will remain unchanged, but as these cells will be of different sizes, the resulting latitudes, longitudes and diagonals will not necessarily be straight lines. The initially square cells will become regular or irregular quadrilaterals, (excluding complex quadrilaterals).
3/ The distances measured orthogonally between opposite sides of the resulting magic or semi-magic square viewpoints will always be √45, (the circumferences of the magic torus).
This third rule took into account the flattened square that we are accustomed to looking at, but it also implied that the torus would degenerate into a sphere... With these new constraints, on the 6th January 2017 I was able to come up with the area magic torus illustrated below:
These extended best wishes, expressed through the complete set of third-order magic and semi-magic squares, include messages that reflect the multiple nationalities of the members of the magic square circle. The magic square viewpoint of the torus is placed at the top left. The patterns still need adjusting in order to achieve the correct areas, but as there is more flexibility, I am fairly confident that at least one accurate solution can be found.
On the 6th January 2017
Walter Trump also sent us a new area magic design that used 4 continuous straight dissection lines. Although this schema could not be adapted to the number sequence 1 to 9, it was area magic:
 |
| Area Magic Schema by Walter Trump |
Inder Jeet Taneja then suggested that the problem with the sequence 1 to 9 was that the total areas did not add up to a perfect square area. He proposed that instead of using the numbers 1 to 9, perhaps we should try using the numbers 5 + 6 + ... + 13 = 81 = 9² ?
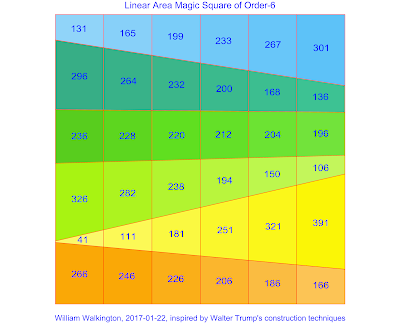
On the same day, following Inder's suggestion, Walter Trump amazed us all with this first third-order linear area magic square! :
Bravo Walter for your achievement following Inder's suggestion! I hardly dared to believe that such a simple area pattern could produce a magic square!
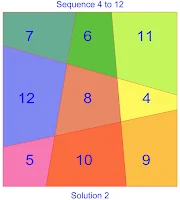
Having other commitments to honour, Walter Trump then requested that somebody else searched for solutions using lower sequences. No other volunteers came forward, so I decided to look for myself, and came up with this second linear area magic square of the third-order using the sequence 3 to 11:
As I am not a programmer, I used Autocad to construct this linear area magic square manually. The areas of this provisional square are therefore only accurate up to two decimal places, before computer verification and area optimisation.
In the meantime Walter Trump continued writing a computer program to handle the equations and search iteratively for solutions. This was able to give orthogonal coordinates having at least 14 decimals after the commas. At first unable to solve the non-linear equations explicitly, Walter progressively improved his approach, and on the 8th January 2017 he sent us a message stating that for some sequences there were two solutions, and that the lowest number sequence ranged from 2 to 10!
On the 10th January 2017, Walter Trump created an algorithm for
"Third-Order Linear Area Magic," which he has kindly authorised me to publish below. This explains the method of construction and gives the reason why two solutions exist for most, but not all of the sequences studied:
Using the coordinates generated by Walter Trump's computer program, both solutions of the 5 lowest sequences of the third-order linear area magic squares are illustrated in square form below. It will be seen that the 1 to 9 sequence fails, and the linear area magic squares are only possible from the sequence 2 to 10 upwards (when the continuous straight dissection lines produce no more than 4 intersections inside the squares):
During this time my first question concerning the sequence 1 to 9 remained unanswered. So, on the 9th January 2017, I created the first area magic square that used the numbers of the classical magic square of order-3, as illustrated below:
More recreational than mathematical, this
"Mont Saint Michel" area magic square demonstrates that it is possible to use 2 continuous straight dissection lines - thus resolving the initial 2017 greetings card challenge. The design is an area magic square, because all of the cells are quadrilaterals (even if near triangular for the area 1), and all of their connections are preserved.
This is an ongoing story, and there will probably be new developments in the near future. Apart from Inder Taneja, Lee Sallows and Walter Trump who I have already mentioned, I also wish to thank the other participants: These include
Craig Knecht for his kind encouragements,
Miguel Angel Amela for his encouragements and suggestions concerning accuracy,
Dwane Campbell for his encouragements and suggestions, and last but not least,
Francis Gaspalou for his encouragements and interventions: For the area magic squares of the third-order, Francis Gaspalou wrote the equations of the 4 straight lines using 4 parameters which were the 4 slopes of those lines. He found the exact conditions which had to be fulfilled by these 4 parameters in order to obtain a solution. Unfortunately it was not possible to solve the system and write explicit formulae for the solutions. Francis was nevertheless able to check that the two solutions per sequence found by Walter Trump's algorithm fulfilled the conditions. Thus by using this different method, Francis was able to confirm the validity of Walter's computer results. Francis Gaspalou has kindly authorised me to publish
his equations here:
On the 13th January 2017
Bob Ziff intervened, stating that if we agree that the system of equations is soluble, then it is soluble to any number of digits, and proved his point by calculating the slopes with 1000 digits, using the professional software Mathematica and the four equations of Francis Gaspalou.
Also, on the 13th January 2017, Walter Trump created a third-order linear area nearly-magic square with integer coordinates. This square is semi-magic with a magic constant of 940800! Walter points out that when you divide all the areas by 140, then the coordinates are no longer integers, but irrational numbers that can be exactly described using fractions and square roots. Walter has kindly authorised me to publish
his findings below:
Francis Gaspalou has suggested that the next step might be to find a fourth-order area magic square with 6 continuous straight dissection lines, or even a concentric fifth-order area magic square. Why not imagine a contest, open to all, so as to find higher-order solutions of an equal mathematical importance to that of the third-order linear area magic squares?
If anyone wishes to contribute linear or other strict geometrical constructions of higher-order area magic squares, then please send me the x and y coordinates of the cell intersections that define the areas correctly up to two or more decimals after the commas. No prizes can be given, but the authors of pertinent solutions will, if they wish, have their solutions published here, and thus be able to bask in the reflected glory...
Latest developments
On the 19th January 2017
Greg Ross published an article on the subject of Area Magic Squares in his
Futility Closet - An Idler's Miscellany of Compendious Amusements. This article has since been relayed by
Reddit Mathpics,
Simplementenumeros,
Prime Puzzles, and by
Thermally Stressed Dairy Cows, amongst others.
On the 20th January 2017 I was aware that Walter Trump, (now joined by
Hans-Bernhard Meyer), had already found that there are no cases of order-4 area magic squares with sequences of consecutive numbers. So I therefore began searching for non-consecutive number sequences that might also yield solutions in order-3, and produced the draft linear area magic square illustrated below:
I sent this square to Walter Trump and the other members of the magic square circle asking if it could be verified using a computer program. Walter was quick to react, sending me precise coordinates for two solutions. Drawn-up using his coordinates, the two versions of this square are illustrated below:
On the 3rd February 2017, responding to a
Prime Puzzle challenge, Jan van Delden contributed the following palprime linear area magic square solution:
The palindromic primes used here are symmetrical numbers that remain the same when their digits are reversed. The magic sum of these 11-digit palindromic primes is 377,024,295,63. This area magic square is the conversion of a square that was originally sent by
Carlos Rivera and Jaime Ayala to
Harvey Heinz on the 22nd May 1999. Jan van Delden mentions that the direction coefficients of the lines are indicated in white, and that the quadrilaterals are numbered in the style of Francis Gaspalou. Full details of Jan van Delden's approach to the equations can be found in
Prime Puzzles.
On the 4th February 2017 Jan van Delden contributed this second prime linear area magic square to Prime Puzzles:
Jan states that this prime area magic square has a minimal magic sum of S=213. Congratulations Jan, for these prime achievements!
Please note, that since the 5th March 2017, Jan has published a new paper entitled "Area Magic Squares of Order 3," in which he extends his findings.
Seemingly, the number of order-3 linear area squares is infinite!
Related links
On the same day
Hans-Bernhard Meyer published an article entitled
Observations on 4x4 Area Magic Squares with vertical lines in his website: Math'-pages.
Since the 3rd February 2017,
Walter Trump has published a chapter entitled
Area Magic Squares in his website: Notes on Magic Squares. This chapter includes many analyses and examples of area magic squares of the third and fourth-orders.
Since the 8th February 2017,
"Area Magic Squares of Order-4" relates the first findings of area magic squares of the fourth-order.
Since the 11th February 2017,
Inder Jeet Taneja, inspired by the research in area magic squares, has published a new paper entitled
"Magic Squares with Perfect Square Number Sums."
Since the 5th March 2017, Jan van Delden has published a paper entitled
"Area Magic Squares of Order 3" in which he presents an improved algorithm. His work also includes new findings in area
semi-magic squares of order-3, and a shoelace formula to measure the deviation in area.
Since the 8th March 2017, following a tweet by
Simon Gregg, Microsiervos published an article entitled
"Cuadrados de áreas mágicas." This article has been relayed by
Inoreader amongst others.
Since the 22nd March 2017, writing for
EL PAÍS,
Miguel Ángel Morales has included the subject of area magic squares in an article entitled
"No solo de números consecutivos vive el cuadrado mágico."
Since the 19th April 2017, writing for
"Geogebra," Georg Wengler has included an article entitled
"Magisches Flächen-Quadrat."
In the N° 487 2018 May issue of
"Pour La Science" (the French edition of Scientific American), Professor Jean-Paul Delahaye has written an article entitled
"Les Carrés Magiques d'Aires."
In the December 2018 issue of
"Spektrum der Wissenschaft" (a Springer Nature journal, and the German edition of Scientific American), Professor Jean-Paul Delahaye has written an article entitled
"FLÄCHENMAGISCHE QUADRATE."
Since the 25th March 2019, Akehiko Takahashi, the webmaster of "Math Dojo," includes Area Magic Squares in his article entitled
"Magic Squares and Beyond."
On the 17th July 2019, a discussion in Japanese, about Area Magic Squares, began on the forum of
"Japanese Traditional Mathematical Calculator."
Circa 2019, on the French recreational mathematics site
"Diophante," Michel Lafond published the first linear area magic square in a problem n° B138, entitled
"Carré magique géométrique," and asked mathematicians to prove its existence. Several solutions are proposed.
On the 1st January 2020, (exactly three years after the original area magic square greetings card!), an article about area magic patchwork entitled
"Flächenmagische Quadrate - aus Stoff," was published by the German blogger "Siebensachen-zum-Selbermachen."
On the 12th January 2020, the recreational mathematician
Ed Pegg Jr., published a "Magic Square with areas" on his site
"Mathpuzzle."
On the 21st May 2021,
Yoshiaki Araki (面積魔方陣がテセレーションみたいな件
@alytile) tweeted several order-4 and order-3 solutions in
a polyomino area magic square thread. These included (amongst others) an order-4 example constructed with 16 assemblies of 5 to 20 dominoes.
On the 24th May 2021, Yoshiaki Araki then tweeted
an order-3 polyomino area magic square constructed using assemblies of 1 to 9 same-shaped pentominoes!
Edo Timmermans, the author of this beautiful square, had apparently been inspired by Yoshiaki Araki's previous posts!